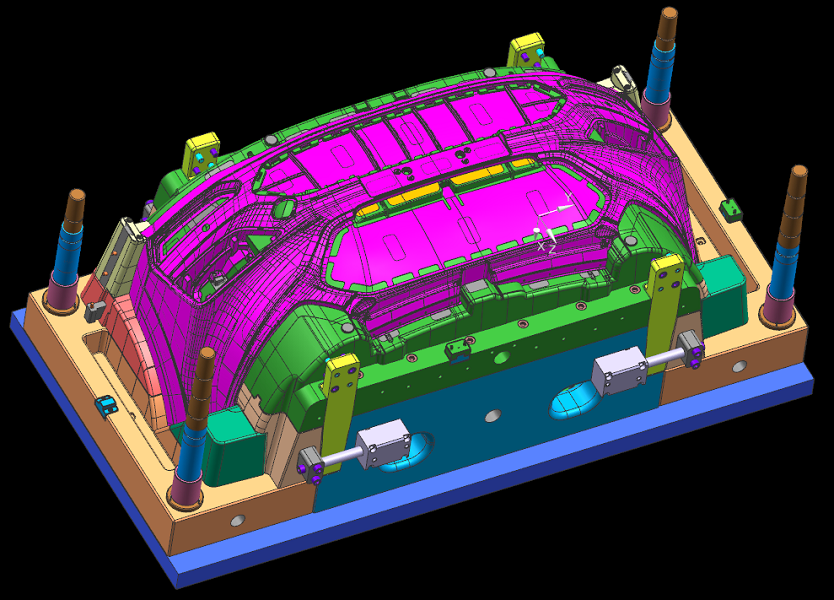
 1. 3D and 2D analysis:
1. 3D and 2D analysis:
In the design process of injection molded products, 3D and 2D analysis are indispensable. Through 3D modeling, designers can more intuitively display the three-dimensional form of products, and thus conduct a comprehensive review of product design. 2D drawings provide a plan view of the product, providing detailed dimensions and technical requirements for subsequent production and manufacturing.
1.1. 3D modeling
3D modeling helps designers comprehensively examine the three-dimensional form of injection molded products, ensuring the completeness of design details.
Through 3D modeling, designers can more intuitively display the three-dimensional form of products, which fully reflects the completeness of design details and provides higher accuracy and reliability for the design of injection molded products.
1.2. 【 2D Drawing Supplement 】
In the design process of injection molded products, we first conduct a detailed analysis of the 3D structure to ensure that the three-dimensional shape of the product meets the design expectations. The 2D drawing complements the 3D design, providing a plan view of the product, clarifying the product's tolerances, appearance details, and material selection.
2. Mold opening direction and parting line:
For each injection molded product, the mold opening direction and parting line must be clearly defined in the initial design stage. This step is crucial as it directly affects the manufacturing process and appearance quality of the product.
2.1. Mold opening and parting line design
The reasonable design of the mold opening direction and parting line determines the manufacturing process and appearance quality of the product, which can reduce the dependence on the core pulling slider mechanism and thus lower the mold cost. By designing a reasonable mold opening direction, the need for core pulling can be reduced, further extending the service life of the mold.
2.2. Draft angle and design elements
The draft angle is an important design element that helps prevent demolding issues and ensures the surface and mechanical accuracy of the design. In order to prevent the product from being pulled during the demolding process, we need to ensure an appropriate demolding slope.
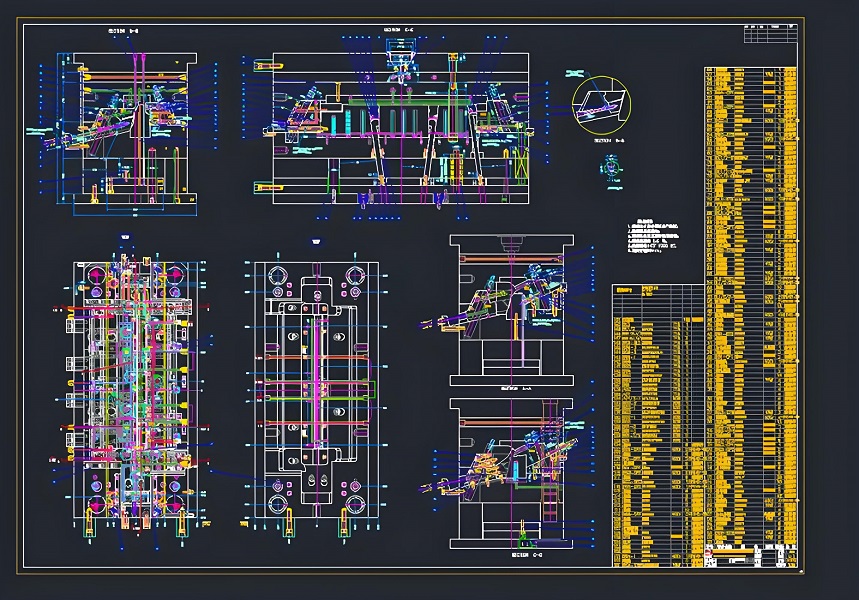 3. Product design elements:
3. Product design elements:
3.1. Wall thickness and reinforcement bars
In the design of injection molded products, controlling wall thickness and reinforcing rib design are very important. The uneven distribution of wall thickness and improper design can cause various problems, such as surface shrinkage, porosity, and the formation of weld lines, which must be optimized through structural adjustments.
3.2. Rounded corners and other designs
In product design, rounded corner design can effectively improve the processing efficiency of molds and avoid problems caused by stress concentration. In addition, different fillet designs may affect the position of the parting line, so it is necessary to choose the appropriate fillet according to the specific situation.
3.3. Hole design and core pulling slider
The design of holes and the structure of core pulling sliders have a direct impact on the complexity of injection molded products. The shape of the hole is usually designed in a circular shape, and its axial direction is ensured to be consistent with the mold opening direction to avoid core pulling problems.
4. Embedded and identification design:
4.1. [Insert Design and Function]
In injection molded products, inserts can enhance local strength and hardness. In the design, it should be ensured that the embedded parts will not rotate or be pulled out in the plastic, for example, through designs such as embossing and holes.
4.2. Logo Design and Accuracy
The design of product identification has special requirements during the injection molding process. The identification is usually placed in a flat area on the inner surface to ensure consistency between its normal direction and the mold opening direction, thereby ensuring injection molding accuracy.
5. Deformation issues and buckle design:
5.1. Reasons and solutions for deformation of injection molded parts
During the injection molding process, due to uneven shrinkage of the plastic, the injection molded parts are prone to deformation problems. To reduce the occurrence of this problem, effective control needs to be achieved through material selection and process optimization.
5.2. Secure and precise buckle design
Reasonable design can enable multiple buckles to share functions, which not only ensures stability, but also puts high demands on tolerance control to extend service life.
6. Welding and Balancing Process:
6.1. Application of Welding Technology
In the manufacturing of injection molded products, the application of welding technology helps to improve the connection strength of the product structure, while also simplifying the design process to improve production efficiency.
6.2. Balancing Process and Performance
In actual production, it is necessary to reasonably consider the relationship between process requirements and product performance, and improve production efficiency by optimizing process parameters while ensuring product quality.
7. Screw post and BOSS design:
7.1. Key points of screw column design
In the design of injection molded products, the design of screw columns emphasizes the stability of their structure, while avoiding the use of separate or designed columns far away from the outer wall to prevent various problems during the molding process.
7.2. BOSS Design Details
The design of BOSS needs to pay attention to the rationality of geometric shape and processing convenience, while also paying attention to the relationship between its position and product wall thickness to ensure product strength and connection stability.
 1. 3D and 2D analysis:
1. 3D and 2D analysis: 3. Product design elements:
3. Product design elements: